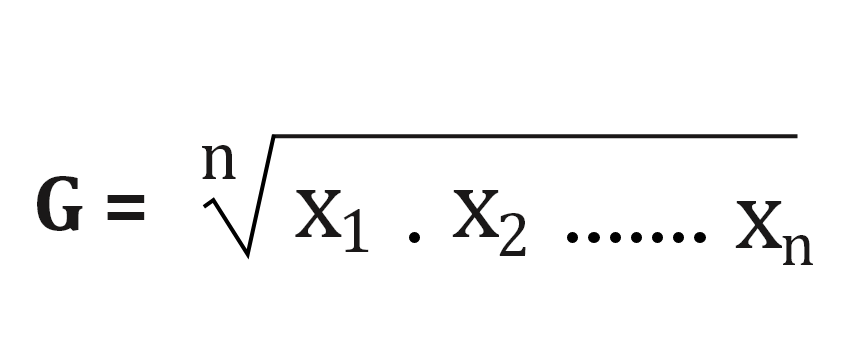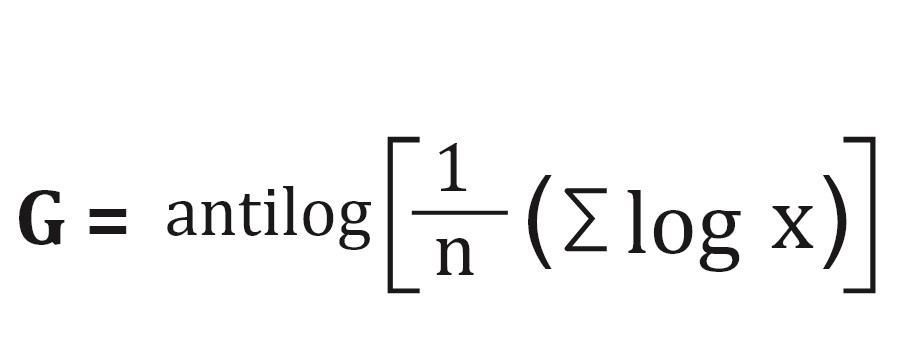This geometric mean calculator evaluates the geometric mean of the entered values; it also provides step-by-step calculations.
What is geometric mean in statistics?
A geometric mean is a type of average, defined as the nth positive root of the product of the terms of the data set.
Formula of Geometric mean:
There are two different formulas to calculate the geometric mean of the given data:
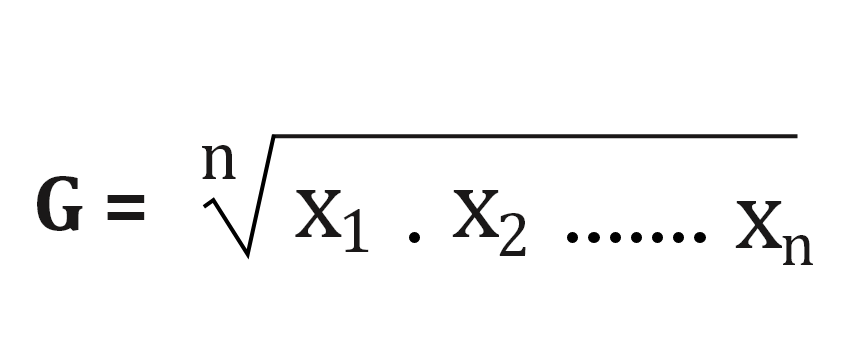
In the above formula:
- X1, X2, X3, …. , Xn
- “n” is the total number of terms
When “n” is very large we use the following formula:
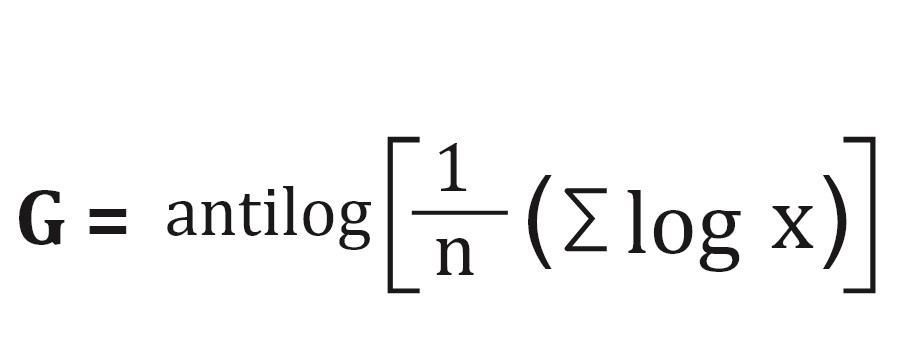
- “Σ (log X)” is the sum of the logarithm of the values.
How to Calculate Geometric Mean?
Below is an example for calculating the geometric mean of ungrouped data.
Example
10, 12, 18, 20, 25, 30, 35
Solution:
Step 1: Extract the data.
X = 10, 12, 18, 20, 25, 30, 35
n = 7
Step 2: Put the values in the formula.
Geometric mean = (X1 * X2 . . .* Xn)1/n
Geometric mean = (10 * 12 * 18 * 20 * 25 * 30 * 35)1/7
Geometric mean = (1134000000) 0.1429
Geometric mean = 19.6570